Brain Facts
The brain is the specialized organ that literally coordinates everything we think, feel, and do. It is made up of cells called neurons, which communicate with each other through electrical impulses (known as brainwaves) and chemicals (neurotransmitters).
When we experience traumas, a disruption in the neuro-electric communication system takes place. Neurons then receive too much or not enough of the signals that help them run smoothly.
Different Lobes for Different Activities
The brain is divided into different sections, which are each responsible for different tasks. The brain is also separated into two hemispheres that work in conjunction with the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems of the autonomic nervous system. When the brain is operating smoothly, the lobes and hemispheres work to support each other in task and function.
In brains that are out of balance, activity levels in the various lobes are not appropriate to support tasks the person is trying to accomplish. This results in negative experiences over which we have little control. We might feel constantly anxious, worried, or sad. We may have troubling thoughts that constantly intrude into our days and nights. We may lose motivation for accomplishing goals and dreams. We might have trouble paying attention at school or work. And, after a full, exhausting day of trying to work with a non-optimized brain, we find that we still have difficulty sleeping at night.
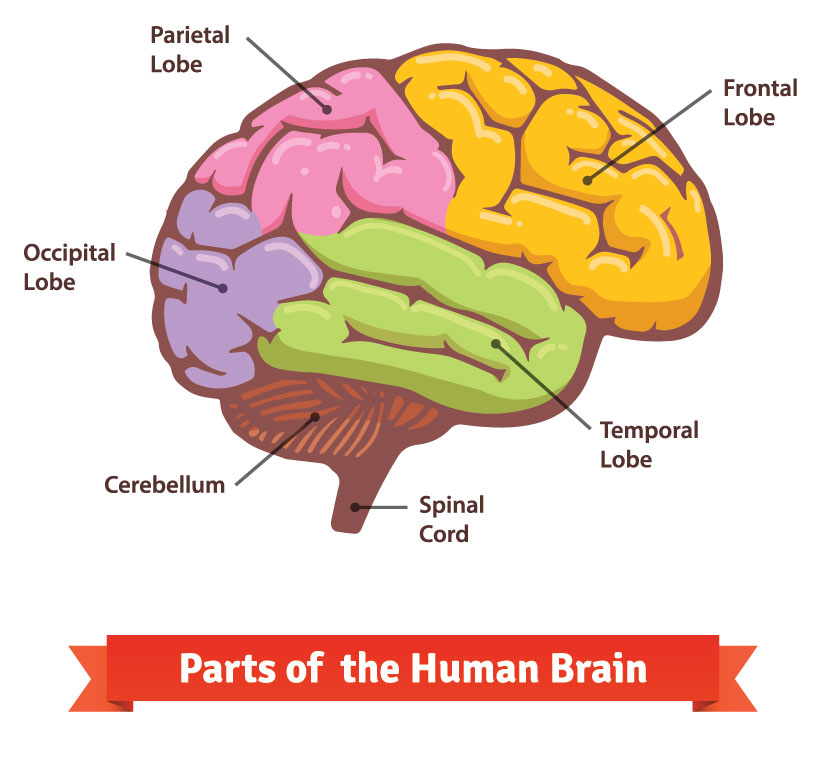
Although not an inclusive list, here are some general tasks each area of the brain is responsible for:
- Temporal : Language comprehension and speech production, retention of visual memories, storing new memories, and processing sensory input
- Parietal: Language processing, integration of sensory information related spatial awareness, receives information through the sense of touch including temperature and pain.
- Occipital: Involved in all aspects of vision and visual processing; contains the Visual Cortex; interprets color; spatial mapping of visual stimuli; involved in calming activities to promote sleep.
- Cerebellum: Responsible for coordination, equilibrium, and balance; precision, and timing of movement; integrates information for the planning of fine motor movements; motor learning.
- Frontal: Critical for higher level activities, such as maintaining attention to task, formation of short term memories, ability to plan tasks and organize information; involved with motivation and follow through
- Corpus Callosum: Allows for communication between the right and left hemispheres.
Neurons
Neurons are the cells that make up the brain. These cells communicate with each other by sending and receiving electrical and chemical messages back and forth. All of your thoughts, movements, and activities are the result of this communication.
Brainwaves
Brainwaves are the electrical impulses that allow neurons to “talk” to each. Electrical impulses originate in one neuron as a response to the outside world. The impulse travels down the axon of the neuron to reach the dendrite of other cells. At this point, neurotransmitters (chemicals that help with brain function ) can be released by one cell or absorbed by another. The process then repeats until the desired outcome (such as scratching your nose in response to an itch) is complete.
Brainwaves travel at different speeds (frequency) and are measured in Hertz (Hz). Just the way each lobe of the brain has a specific function; different speeds of brainwave activity are utilized for different tasks.
- Delta – Related to deep sleep; basic body functions
- Theta – Subconscious, emotions, and memories
- Alpha – Relaxed, meditative, and creative function
- Beta – Alert and working; thinking and solving problems
- Gamma – Not well understood; high level perception, consciousness
When the electrical impulses of the brain happen too quickly or too slowly, improper amounts of neurotransmitters are released. This results in dysfunctional or improper responses to the environment (such as being sad for no reason; constant worrying; not being able to pay attention in class; not being motivated to work on goals; etc).
NeurOptimal ® Brain Spa sessions are effective in helping the brain correct these imbalances and return to an ideal state of function.